HowTo Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Configure The Network Card
[b] Command line text based GUI tool (No X Windows/Gnome/KDE required) - system-config-network
[c] Edit configuration files stored in/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory. This method works with remote server over the ssh based session.
The following instructions are tested and compatible with:
- Cent OS Linux v3/4/5.x.
- Fedora Core Linux (older version).
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) v3/4/5.x based server.
Method # 1: GUI tool system-config-network
Open the X terminal or login using ssh over X based session command (ssh -X user@server-name-here). Type the following command at shell prompt:
Warning: It is important that you configure network interface cards correctly over ssh -X based session; otherwise, you will be locked out due to wrong network configuration.
$ system-config-network &Sample outputs:
You will see a Window as above. Next, select your Ethernet card (such as eth0 or eth1) and click on the Edit button. You can now setup/modify IP address, netmask, default gateway and other properties. Here is an example from my personal RHEL 5.x server:
You can obtain IP address using DHCP or setup manually. Once IP address assigned, click onOk button to save the changes. You can activate card by clicking on Activate button.
Method # 2: Command line tool system-config-network-tui
If you don't have X windows GUI (gnome/kde desktop) installed on RHEL/CentOS/Fedora based system, than type the following command at shell prompt (this method also works on remote server using ssh based session):
Warning: It is important that you configure network interface cards correctly over ssh based session; otherwise, you will be locked out due to wrong network configuration.
# system-config-network-tui &Sample outputs:
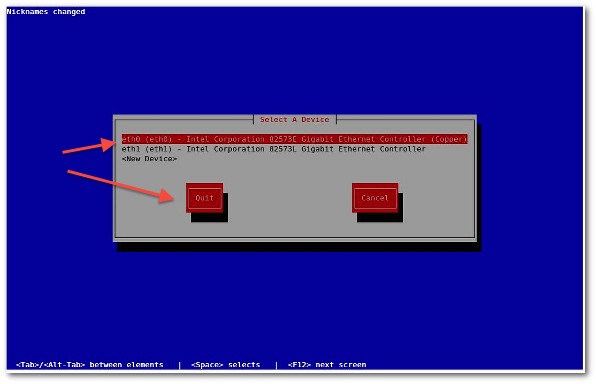
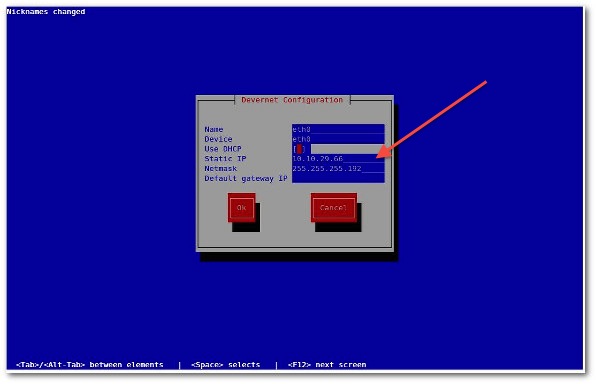
Select your Ethernet card such as eth0 or eth1 and hit [Enter] or [F12] special key to configure IP properties for selected NIC:
You can obtain an IP address using DHCP or setup IP address manually. Once an IP address assigned, click on the Ok button to save the changes.
Method #3: Edit configuration files stored in/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory
You can configure network card by editing text files stored in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory. Open the terminal or login using ssh. Next, change directory to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/:
You need to edit / create files as follows using a text editor such as vi:
# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/You need to edit / create files as follows using a text editor such as vi:
- /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 : First Ethernet card configuration file.
- /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1 : Second Ethernet card configuration file.
Examples: Edit eth0 configuration file
To edit/create first NIC file, type the following command in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory:
Warning: It is important that you configure network interface cards correctly over ssh based session; otherwise, you will be locked out due to wrong network configuration.
# vi ifcfg-eth0OR
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0Edit or modify as follows for static ip configuration:
# eth0 - Intel Corporation 82573E Gigabit Ethernet Controller (Copper) on server1.cyberciti.biz by nixCraft on 10/4/2007 DEVICE=eth0 BOOTPROTO=static DHCPCLASS= HWADDR=00:30:48:56:A6:2E IPADDR=10.10.29.66 NETMASK=255.255.255.192 ONBOOT=yes
Save and close the file.
Setting up default gateway and server (host) name
You need to define a default gateway (router IP) and hostname in /etc/sysconfig/network file. Edit /etc/sysconfig/network, enter:
Append or modify configuration as follows:
# vi /etc/sysconfig/networkAppend or modify configuration as follows:
NETWORKING=yes HOSTNAME=www1.nixcraft.in GATEWAY=10.10.29.65
Save and close the file. Finally, you need to restart the network service, run:
OR
# /etc/init.d/network restartOR
# /sbin/service network restartSetting up dns server
Make sure you have correct DNS server defined in /etc/resolv.conf file:
Setup DNS server IP address as follows (feel free to replace 10.0.80.11, 10.0.80.12 as per your setup):
Save and close the file. Now you can ping the gateway/other hosts using the ping command:
Sample outputs:
# vi /etc/resolv.confSetup DNS server IP address as follows (feel free to replace 10.0.80.11, 10.0.80.12 as per your setup):
nameserver 10.0.80.11
nameserver 10.0.80.12
nameserver 202.67.222.222Save and close the file. Now you can ping the gateway/other hosts using the ping command:
$ ping 10.0.80.12Sample outputs:
PING 10.0.80.12 (10.0.80.12) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.80.12: icmp_seq=1 ttl=251 time=0.972 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.80.12: icmp_seq=2 ttl=251 time=1.11 ms
You can also check for Internet connectivity with the ping, nslookup and/or host command:
Sample outputs:
$ nslookup cyberciti.bizSample outputs:
Server: 10.0.80.11 Address: 10.0.80.11#53 Non-authoritative answer: Name: cyberciti.biz Address: 75.126.43.232
You can also use host dns lookup command as follows:
Sample outputs:
$ host nixcraft.inSample outputs:
nixcraft.in has address 75.126.43.232 nixcraft.in mail is handled by 10 mail.nixcraft.in.
How do I see or debug network configuration on RHEL/CentOS based server?
Simply use any one of the following commands:
########################### ## display ip config ## ########################### ifconfig ifconfig -a | more ifconfig eth0 ifconfig eth1 ip link ip addr ########################### ## display routing table ## ########################### route route -nr route -nr|more ip route ########################### ## display dns config ## ########################### cat /etc/resolv.conf ########################### ## display firewall config# ########################### iptables -L -n -v | more cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables ########################### ## Debug network issues # ########################### ping host-name-here ping ip-addeess-here host ip-address-here host domain-name-here traceroute host-name-here mtr host-name-here dmesg | grep eth lspci | grep -i eth


No comments:
Post a Comment