How To Patch and Protect Linux Server Against the Glibc GHOST Vulnerability # CVE-2015-0235
A very serious security problem has been found and patched in the GNU C Library called Glibc. It was announced on 27th January 2015.
What is the GHOST security bug?
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Easy (rss) |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux+reboot required |
| Estimated completion time | 10m |
From the RHEL bugzilla:
A heap-based buffer overflow was found in __nss_hostname_digits_dots(), which is used by the gethostbyname() and gethostbyname2() glibc function call. A remote attacker could use this flaw to execute arbitary code with the permissions of the user running the application.
A mailing list entry with more details, including in-depth analysis and exploit vectors is here.
What C library (Glibc) version does my Linux system use?
The easiest way to check the version number is to run the following command:
ldd --version
Sample outputs from RHEL/CentOS Linux v6.6:
ldd (GNU libc) 2.12
Copyright (C) 2010 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Written by Roland McGrath and Ulrich Drepper.
Sample outputs from Ubuntu Linux 12.04.5 LTS:
ldd (Ubuntu EGLIBC 2.15-0ubuntu10.9) 2.15
Copyright (C) 2012 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Written by Roland McGrath and Ulrich Drepper.
Sample outputs from Debian Linux v7.8:
ldd (Debian EGLIBC 2.13-38+deb7u6) 2.13
Copyright (C) 2011 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Written by Roland McGrath and Ulrich Drepper.
A list of affected Linux distros
- RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) version 5.x, 6.x and 7.x
- CentOS Linux version 5.x, 6.x & 7.x
- Ubuntu Linux version 10.04, 12.04 LTS
- Debian Linux version 7.x
- Linux Mint version 13.0
- Fedora Linux version 19 or older
- SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 and older (also OpenSuse Linux 11 or older versions).
- Arch Linux glibc version <= 2.18-1
GHOST vulnerability check
You can test or reproduce the bug using the following C code:
/* ghosttest.c: GHOST vulnerability tester */ /* Credit: http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2015/01/27/9 */ #include <netdb.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #define CANARY "in_the_coal_mine" struct { char buffer[1024]; char canary[sizeof(CANARY)]; } temp = { "buffer", CANARY }; int main(void) { struct hostent resbuf; struct hostent *result; int herrno; int retval; /*** strlen (name) = size_needed - sizeof (*host_addr) - sizeof (*h_addr_ptrs) - 1; ***/ size_t len = sizeof(temp.buffer) - 16*sizeof(unsigned char) - 2*sizeof(char *) - 1; char name[sizeof(temp.buffer)]; memset(name, '0', len); name[len] = '\0'; retval = gethostbyname_r(name, &resbuf, temp.buffer, sizeof(temp.buffer), &result, &herrno); if (strcmp(temp.canary, CANARY) != 0) { puts("vulnerable"); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } if (retval == ERANGE) { puts("not vulnerable"); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } puts("should not happen"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
Compile and run it as follows:
$ gcc ghosttest.c -o ghosttest $ ./ghosttest
Sample outputs from patched Debian v7.8 server:
not vulnerable
Sample outputs from unpatched Ubuntu 12.04 LTS server:
vulnerable
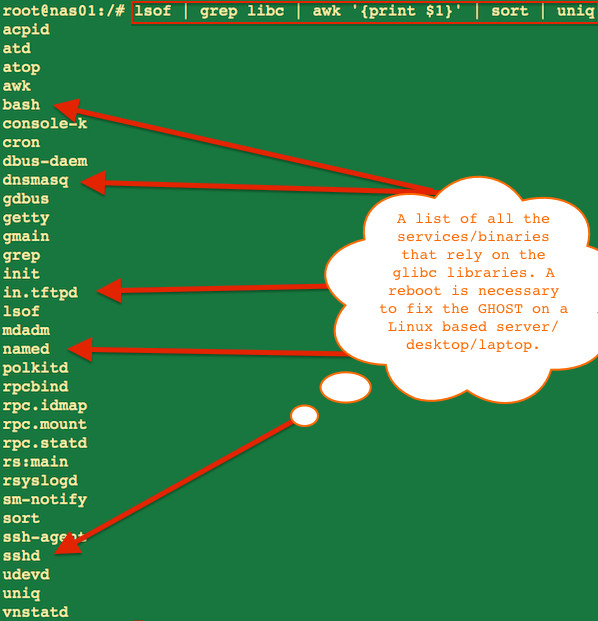
How do list packages/applications depends upon vulnerable Glibc?
Type the following lsof command:
lsof | grep libc | awk '{print $1}' | sort | uniq
Sample outputs from my Debian Linux v7.x nas:
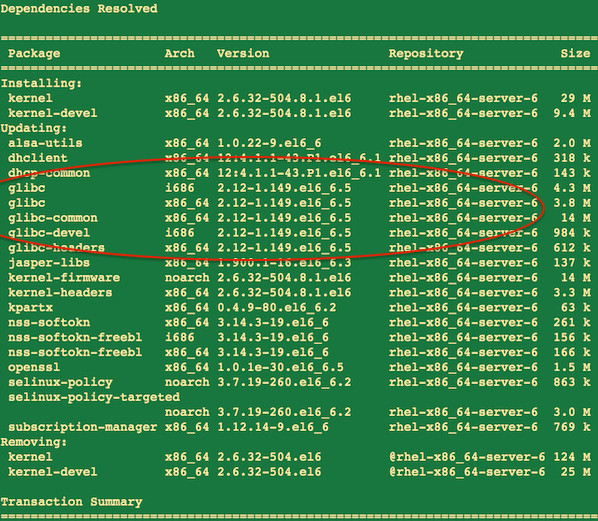
Fix the GHOST vulnerability on a CentOS/RHEL/Fedora/Scientific Linux
Type the following yum command as the root user:
sudo yum clean all sudo yum update
Finally, reboot RHEL/SL/Fedora/CentOS Linux server by typing the following command:
### Sysadmin should plan on updating as soon as possible or use maintenance reboot window ## sudo reboot
Sample outputs:
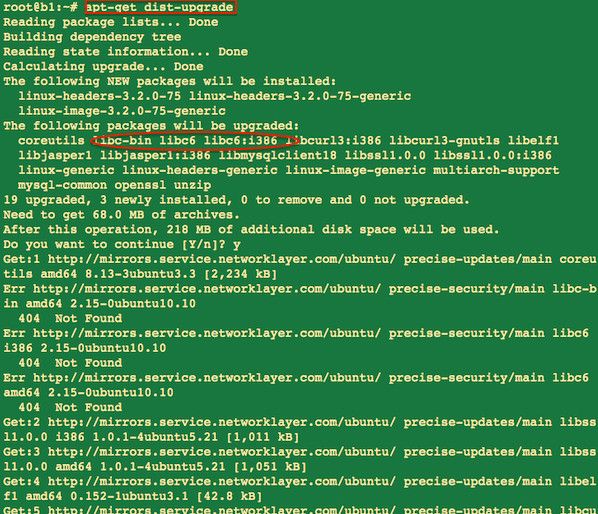
Fix the GHOST vulnerability on a Ubuntu Linux
Type the following apt-get command as the root user:
sudo apt-get clean sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
Finally, reboot Ubuntu Linux server by typing the following command:
sudo reboot
Sample outputs:
Fix the GHOST vulnerability on a Debian Linux
Type the following apt-get command as the root user:
sudo apt-get clean sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
Finally, reboot Debian Linux server by typing the following command:
sudo reboot
Sample session:
How can I verify that my Linux system no longer vulnerable after the reboot?
Method #1: The easiest way to check vulnerability and/or confirm remediation is to run the following command to verify that you are running an updated version of Glibc:
$ ldd --version
Method #2: Run the instructions given in the previous section called GHOST vulnerability check (generic method for all Linux based systems).
Method #3: If you are RHN subscriber see the Red Hat Access Lab: GHOST tool (only for RHEL/CentOS/SL systems:
#!/bin/bash # rhel-GHOST-test.sh - GHOST vulnerability tester. Only for CentOS/RHEL based servers. # # Credit : Red Hat, Inc - https://access.redhat.com/labs/ghost/ # vercomp () { if [[ $1 == $2 ]] then return 0 fi local IFS=. local i ver1=($1) ver2=($2) # fill empty fields in ver1 with zeros for ((i=${#ver1[@]}; i<${#ver2[@]}; i++)) do ver1[i]=0 done for ((i=0; i<${#ver1[@]}; i++)) do if [[ -z ${ver2[i]} ]] then # fill empty fields in ver2 with zeros ver2[i]=0 fi if ((10#${ver1[i]} > 10#${ver2[i]})) then return 1 fi if ((10#${ver1[i]} < 10#${ver2[i]})) then return 2 fi done return 0 } glibc_vulnerable_version=2.17 glibc_vulnerable_revision=54 glibc_vulnerable_version2=2.5 glibc_vulnerable_revision2=122 glibc_vulnerable_version3=2.12 glibc_vulnerable_revision3=148 echo "Vulnerable glibc version <=" $glibc_vulnerable_version"-"$glibc_vulnerable_revision echo "Vulnerable glibc version <=" $glibc_vulnerable_version2"-"$glibc_vulnerable_revision2 echo "Vulnerable glibc version <=" $glibc_vulnerable_version3"-1."$glibc_vulnerable_revision3 glibc_version=$(rpm -q glibc | awk -F"[-.]" '{print $2"."$3}' | sort -u) if [[ $glibc_version == $glibc_vulnerable_version3 ]] then glibc_revision=$(rpm -q glibc | awk -F"[-.]" '{print $5}' | sort -u) else glibc_revision=$(rpm -q glibc | awk -F"[-.]" '{print $4}' | sort -u) fi echo "Detected glibc version" $glibc_version" revision "$glibc_revision vulnerable_text=$"This system is vulnerable to CVE-2015-0235. <https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2015-0235> Please refer to <https://access.redhat.com/articles/1332213> for remediation steps" if [[ $glibc_version == $glibc_vulnerable_version ]] then vercomp $glibc_vulnerable_revision $glibc_revision elif [[ $glibc_version == $glibc_vulnerable_version2 ]] then vercomp $glibc_vulnerable_revision2 $glibc_revision elif [[ $glibc_version == $glibc_vulnerable_version3 ]] then vercomp $glibc_vulnerable_revision3 $glibc_revision else vercomp $glibc_vulnerable_version $glibc_version fi case $? in 0) echo "$vulnerable_text";; 1) echo "$vulnerable_text";; 2) echo "Not Vulnerable.";; esac
Sample outputs from patched RHEL v6.8 server:
bash rhel-GHOST-test.sh Vulnerable glibc version <= 2.17-54 Vulnerable glibc version <= 2.5-122 Vulnerable glibc version <= 2.12-1.148 Detected glibc version 2.12 revision 149 Not Vulnerable.